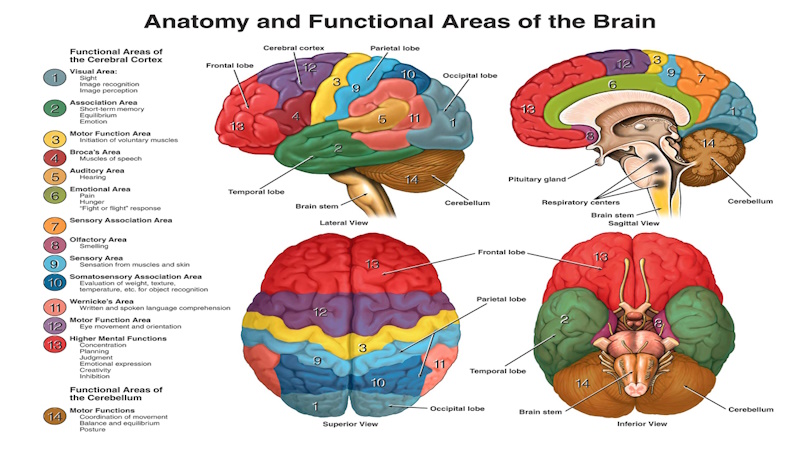
Introduction
The human brain, a marvel of complexity, orchestrates an intricate symphony of neurons, neurotransmitters, and synapses. Unveiling the mysteries of its functioning is not only a scientific pursuit but also holds crucial implications for neurological diseases, with Alzheimer’s disease taking center stage. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the inner workings of the brain, dissect the profound implications in Alzheimer’s, and emphasize proactive prevention strategies to safeguard cognitive health.
The Intricate Dance of Neurons
To commence our journey into the realm of neuroscience, let’s unravel the intricate dance of neurons within the brain.
- Neurons: The Building Blocks of Thought: Neurons, the fundamental units of the nervous system, transmit information through electrical and chemical signals. Their interconnectivity forms the basis of cognition, memory, and all aspects of human consciousness.
- Neurotransmitters as Messengers: Chemical messengers, known as neurotransmitters, play a pivotal role in communication between neurons. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters can lead to disruptions in cognitive functions, potentially contributing to neurodegenerative diseases.
- Synapses: Bridges of Communication: Synapses act as bridges between neurons, allowing electrical impulses and neurotransmitters to traverse the gaps. The efficiency of these synapses is crucial for smooth cognitive functioning.
Consequently, any disruption in this delicate balance can have profound implications, particularly in the context of Alzheimer’s disease.
Unraveling Alzheimer’s Disease
Moving beyond the intricacies of neural communication, let’s focus on the specific implications of these processes in the context of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Alzheimer’s: A Devastating Neurological Disorder: Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein aggregates in the brain, leading to the deterioration of cognitive functions.
- Beta-Amyloid Plaques and Neurofibrillary Tangles: The hallmark signs of Alzheimer’s include beta-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. These aberrant structures disrupt neuronal communication and contribute to the degeneration of brain cells.
- Impact on Memory and Cognitive Abilities: As Alzheimer’s advances, it primarily targets areas associated with memory and cognitive function. This leads to a decline in memory recall, reasoning, and problem-solving skills.
Consequently, understanding the early signs and risk factors is imperative for developing effective prevention strategies.
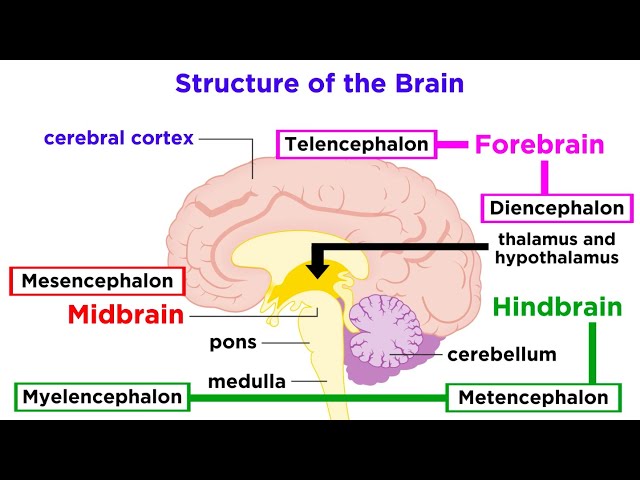
Proactive Prevention Strategies
Shifting our focus towards proactive measures, let’s explore strategies to prevent and mitigate the risk of neurological diseases, including Alzheimer’s.
- Lifestyle Modifications for Cognitive Health: Adopting a brain-healthy lifestyle involves regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, and adequate sleep. These habits promote overall well-being and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
- Mental Stimulation and Cognitive Activities: Engaging in intellectually stimulating activities, such as puzzles, reading, and learning new skills, fosters neuroplasticity—a key factor in maintaining cognitive resilience.
- Social Connectivity and Emotional Well-being: Building and maintaining social connections contribute to emotional well-being, reducing stress levels and bolstering cognitive function. Strong social ties have been linked to a lower risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
- Heart-Healthy Diet: What’s good for the heart is often good for the brain. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids supports cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of conditions that can impact cognitive function.
- Regular Health Check-ups and Cognitive Assessments: Periodic health check-ups, including cognitive assessments, allow for the early detection of potential issues. Early intervention can significantly impact the progression of neurological diseases.
In essence, incorporating these lifestyle changes is not just beneficial for general health but holds the key to preventing neurological diseases.
The Role of Genetics and Research
Beyond lifestyle factors, genetic predisposition and ongoing research also play crucial roles in understanding and preventing neurological diseases.
- Genetic Influences on Neurological Health: While genetics can contribute to the risk of neurological diseases, it’s essential to recognize that lifestyle factors and environmental influences play equally significant roles.
- Advancements in Neurological Research: Ongoing research is shedding light on the intricate mechanisms of the brain and potential therapeutic interventions. Staying informed about these developments is vital for proactive health management.
Consequently, staying abreast of genetic factors and emerging research allows individuals to make informed decisions for their cognitive well-being.
Cultivating a Brain-Healthy Future
Transitioning from understanding the complexities of the brain to practical applications, let’s explore how individuals and communities can collectively cultivate a brain-healthy future.
- Educational Initiatives on Cognitive Health: Promoting awareness and education about cognitive health in schools, workplaces, and communities can empower individuals to make informed choices and adopt brain-healthy habits.
- Community Programs for Mental Well-being: Establishing community programs that prioritize mental well-being fosters a supportive environment. This can include mental health workshops, stress management sessions, and resources for maintaining cognitive health.
In conclusion, embracing a proactive approach to brain health is not just an individual responsibility but a collective effort toward a cognitively resilient society.
Conclusion
The intricate workings of the brain, coupled with the profound implications in neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s, underscore the importance of proactive prevention. By understanding the nuances of neural communication, unraveling the complexities of Alzheimer’s, and implementing lifestyle changes and collective initiatives, individuals can actively safeguard their cognitive well-being. As we navigate the path towards a brain-healthy future, let knowledge, awareness, and a commitment to proactive health be our guiding lights.